Nouns
There is a book on the table.
My father believes in honesty.
I can't forget his kindness.
इन वाक्यों को देखें
Ramu is a farmer.
The cow gives milk. India is a country.
इन वाक्यों में आए शब्द Ramu,farmer और father व्यक्तियों के नाम हैं; cow एक जानवर का नाम है; milk, book और table वस्तुओं के नाम हैं; India और country स्थानों के नाम हैं; honesty और kindness विचार/ भाव के नाम हैं। दुनिया में ऐसे ही हजारों नाम हैं। Grammar की भाषा में इन्हें हम Nouns कहते हैं।
Definition: किसी व्यक्ति, जानवर, स्थान, वस्तु, विचार या भाव के नाम को Noun कहते हैं|
+ A noun is the name of a person, animal, place, thing/feeling or idea.
* A noun is the name of anything.
A noun is a naming word.
ऊपर दी गई परिभाषाओं से यह स्पष्ट है कि Noun एक naming word है। हम जो भी देखते हैं, जानते हैं, सोचते हैं या अनुभव करते हैं, उन सभी के नाम Nouns हैं।
Kinds of the Noun : Noun के पाँच भेद हैं।
1. Proper Noun (व्यक्तिवाचक संज्ञा)
2. Common Noun (जातिवाचक संज्ञा)
3. Collective Noun (समूहवाचक संज्ञा)
4. Material Noun (द्रव्यवाचक संज्ञा)
5. Abstract Noun (भाववाचक संज्ञा)
1. Proper Noun: किसी व्यक्ति, स्थान, जानवर या वस्तु के खास नाम को Proper Noun कहते हैं |
Proper का अर्थ है- one's own.
A proper noun is the name of a particular person, animal,place or thing.
Examples: Ram, Shyam, Geeta, India, Patna, Tom, Moti, Lucy. Yamuna, Ramayana, Bible. Sunday, Monday, January, February, Holi, Id, The Hindustan Times, etc.
2)Common Noun: जिस Noun से किसी खास व्यक्ति, जानवर, स्थान या वस्तु का बोध न होकर पूरी जाति या श्रेणी का बोध होता है, उसे Common Noun कहते हैं Common का अर्थ है- shared by all of the same group.
A common noun is a name given in common to every person, animal, place or thing of the same class or kind.
Examples: boy, girl, cat, dog, bird, snake, man, table, pen, book, river, mountain, town, country, etc
Note: Sita Geeta और Mala से खास लड़कियों का बोध होता है, अतः ये Proper Nouns हैं। परंतु girl कहने से किसी खास लड़की का बोध न होकर किसी भी लड़की का बोध होता है। अतः girl एक Common Noun है।
Leela is a proper noun, but girl is a common noun.
Manoj is a proper noun, but boy is a common noun.
Patna is a proper noun, but city is a common noun.
Bihar is a proper noun, but state is a common noun.
Moti is a proper noun, but dog is a common noun.
India is a proper noun, but country is a common noun.
Yamuna is a proper noun, but river is a common noun.
3. Collective Noun जिस Noun से एक ही तरह के व्यक्तियों या वस्तुओं के समूह का बोध होता है, उसे Collective Noun कहते हैं।
A collective noun is the name of a number of persons or things taken together and spoken of as one whole, [ Examples: class (वर्ग) crowd (भीड़), army (सेना) team (दल), family (परिवार), committee (समुदाय), mob(भीड़),bunch(गुच्छा),flock (झुण्ड) etc.
army' कहने से सैनिकों के समूह का बोध होता है। crowd' कहने से व्यक्तियों के समूह का बोध होता है। इसी प्रकार उपर्युक्त अन्य शब्द किसी न किसी समूह का बोध कराते हैं। अत: वे Collective Nouns हैं।
4. Material Noun- जिस Noun से किसी द्रव्य/पदार्थ का बोध होता है, जिसे मापा या तौला जाता है, किंतु गिना नहीं जाता है, जिससे विभिन्न वस्तुओं का निर्माण होता है, उसे Material Noun कहते हैं।
A material noun is the name of a material substance
Examples: water, milk, wood (लकड़ी), gold (सोना), iron (लोहा), stone (पत्थर), rice. ink, sugar (चीनी), oil (तेल), paper (कागज), ghee, wheat (गहूँ) flour (आटा), bread (रोटी), chalk (खली), meat (मांस), silver (चाँदी), brass (पीतल) pulse (दाल), wool (ऊन)etc.
Note: wood Material Noun , a na Faffa chair, table, bench, house ft Common Nouns bread Material Noun: m एक रोटी के लिए 'a bread' न लिखकर 'a piece of bread' लिखें
5.Abstract Noun: उस गुण, अवस्था, विचार या भाव के नाम को Abstract Noun कहते हैं जिसे देखा या छुआ नहीं जा सकता है, सिर्फ अनुभव किया जा सकता है। An abstract noun is the name of some quality, state,feeling or idea that we can only think of or feel but cannot see or touch.
Examples: goodness , kindness , darkness, foolishness, greatness,sickness, weakness, richness, sweetness,honesty,bravery, wisdom ,beauty, truth, laughter, love, sleep, death,youth,poverty, heat, boyhood, childhood, friendship,etc.
Note: Arts एवं Sciences के नाम भी Abstract Nouns हैं। जैसे grammar,physics, chemistry, music, history, etc.
EXERCISE 1
Direction: Pick out the nouns in the following sentences. Say whether they are proper, common, collective, material or abstract.
Examples:
(a) Ram is the best boy in the class.
Ans. Ram-Proper Noun, boy - Common Noun, class-Collective Noun.
(b) Sympathy is better than gold.
Sympathy-Abstract Noun, gold- Material Noun.
1. Sohan has a red car.
2. Children drink milk.
3. My brother is the captain of the team.
4. Patna is the capital of Bihar.
5. The cat has two eyes.
6.Gandhijee was a great leader of India.
7. The Ganges is a holy river.
8.There is a cap on his hoad.
9. Gold, silver and money cannot buy honesty.
10.The teacher taught me physics and chemistry.
11. Monday is the first day of the week.
12. He has been a good singer since his childhood.
13.Friendship is a boon.
14. Without health there is no happiness.
15. He gave me a bunch of grapes.
16. Ram eats bread, mangoes and sugar.
17. The ring is made of silver.
18. There is a crowd (s) on the road.
19. I have love for my friends.
20. The juice has no sweetness.
EXERCISE 2
Direction: In each of the following groups of words, pick out the noun that belongs to a different class of nouns from the rest.
Examples:
(a) gold, rice, ghee, mango, sand
(b) father, brother, family, son, friend
1. chair, boy, watch, wood, river
2. gold, silver, ring, iron, brass
3. boy, childhood, girl, son, daughter
4. book, paper, pen, student
5. mango, apple, juice, orange
6. table, desk, class, room, chair
7. singer, music , dancer, player
8. milk, ink, tea, coffee, bread, apple
9. teacher, student, class, doctor, boy
10. book, apple, nurse, jug, wood
11. apple, mango, orange, rice, banana.
12. music, bunch, army, crowd, mob
13. class, crowd, team, player, family
14. police, soldier, army, commander.
15. bottle, cup, boy, wine .
16. day, month, year, Sunday, ball
17. death, fear , mob , goodness
18. physics, chemistry, subject, friendship
19. car, petrol, driver, road, book
20. health, disease, pain, doctor
Modern Classification of the Noun
आधुनिक अंग्रेजी व्याकरण (Modern English Grammar) में Nouns को तीन भागों में बाँटा गया है
1. Proper Noun (व्यक्तिवाचक संज्ञा)
2. Countable Noun (गणनीय संज्ञा)
3. Uncountable Noun (अगणनीय संज्ञा)
1. Proper Noun: किसी व्यक्ति, जानवर, स्थान, दिन, महीना, वस्तु, इत्यादि के खास नाम को Proper Nouns कहते हैं।
A proper noun is the name of a particular person. animal, place, day, month or thing.
Examples: Sohan, Tom, Lucy, Nepal, Delhi, Sunday, Monday, January, February, Ganges, Bagmati, Himalayas. Ramayana, Gita, The Times of India, etc.
2. Countable Noun: जिस Noun को हम गिन सकते हैं, उसे Countable Noun कहते हैं।
The noun which can be counted is called the countable noun. .
Examples: cow, dog, class, man, leg, eye, book, star, river, army. state, girl, child, student, etc.
3. Uncountable Noun: जिस Noun को हम नहीं गिन सकते हैं, उसे Uncountable Noun कहते हैं।
* The noun which cannot be counted is called the uncountable noun.
Examples: oil, water, rice, bread, butter, flour, wheat, brass, . silver, love, beauty, honesty, truth, boyhood, childhood, youth. kindness, goodness, friendship knowledge (ज्ञान), courage (हिम्मत), fear (डर), etc.
Note: 1. Uncountable Noun के पहले न तो a/an का प्रयोग होता है, न ही इसका Plural Form होता है। अर्थात् a oil. a water, oils, wheats, इत्यादि लिखना गलत होगा। अगर कहीं Plural Form बनता भी है, तो उसके अर्थ में परिवर्तन होता है।
2. Countable Noun के पहले a/an का प्रयोग होता है और इसका Plural Form होता है। जैसे a boy, boys, an ant, ants.
3. हिंदी भाषा में रोटी एक गणनीय संज्ञा है, परंतु अंग्रेजी भाषा में bread Uncountable Noun है। अत: आम एक रोटी की अंग्रेजी' bread' न लिखकर "a piece of bread" लिखें चार रोटियों four pieces of bread.
ध्यान में रखें
पुराने(Old) Grammar के अनुसार
Noun के भेद
1. Proper Noun
2. Common Noun
3. Collective Noun
4. Material Noun
5. Abstract Noun
आधुनिक(Modern) Grammar के अनुसार
Noun के भेद
1. Proper Noun
2. Countable Noun
3. Uncountable Noun
EXERCISE 3
Direction: Pick out the nouns in the following sentences. Say whether they are proper, countable or uncountable.
Example: Mr Chopra is a man of great knowledge.
Ans. Mr Chopra - Proper Noun, Man-Countable Noun.,
Knowledge - Uncountable Noun.
1. The cow is an animal.
2. A dog has four legs.
3. Ram is a student of this school.
4. Mumbai is a big city of India.
5. There are milk, rice, bread and oranges on the table.
6. A week has seven days.
7. The students are reading books in the class.
8. Children have honesty.
9. The Ganges is a river.
10. I have love for my friends.
11. This chair is made of wood.
12. An apple is good for health.
13. The little girl has no fear.
14. He has kindness and greatness.
15. Our army showed great courage in the battle last year.
16. His son is the captain of the team.
17. I like the music of India.
18. The Gita and the Ramayana are holy books.
19. My friend does not take coffee or tea in the morning.
20. He has been a good singer since his childhood.
Pronouns
इन वाक्यों को देखें
Ram is a student. He reads in class VI.
Sita is a dancer. She is very beautiful.
My father has a car. It is red.
The boys are absent today. They will come tomorrow.
इन वाक्यों में आए शब्द He, She, It और They पर विचार करें। ये किसी-न-किसी Noun के बदले में प्रयुक्त हुए हैं। He का प्रयोग Ram के बदले में, She का प्रयोग Sita के बदले में, It का प्रयोग car के बदले में और They का प्रयोग boys के बदले में हुआ है। ऐसे शब्दों को Grammar की भाषा में Pronouns कहते हैं।
Definition: Pronoun वह शब्द है जो किसी Noun के बदले में प्रयुक्त होता है।
* A pronoun is a word used instead of a noun.
* A pronoun stands for a noun.
Pronoun की परिभाषा से स्पष्ट है कि यह Noun का substitute है। जब हम किसी कारणवश Noun का प्रयोग करना नहीं चाहते, तब उस Noun के बदले उपयुक्त Pronoun का प्रयोग करते हैं। Pronoun की उपयोगिता को समझने के लिए इन वाक्यों पर विचार करें.
Ram is my friend. Ram reads in my class. Ram is absent today, because Ram is ill.
यहाँ Ram (Noun) का प्रयोग बार-बार होने से संपूर्ण expression भद्दा-सा लगता है। अगर दूसरे और तीसरे वाक्य में Ram के बदले He का प्रयोग करें, तो यह भद्दापन समाप्त हो जाएगा -
Ram is my friend. He reads in my class. He is absent today because he is ill.
Kinds of the Pronoun: Pronoun के निम्नलिखित प्रमुख भेद हैं .
1. Personal Pronoun
2. Possessive Pronoun
3. Reflexive Pronoun
4. Emphatic Pronoun
5. Demonstrative Pronoun
6. Indefinite Pronoun
7. Distributive Pronoun
8. Reciprocal Pronoun
9. Relative Pronoun
10. Interrogative Pronoun
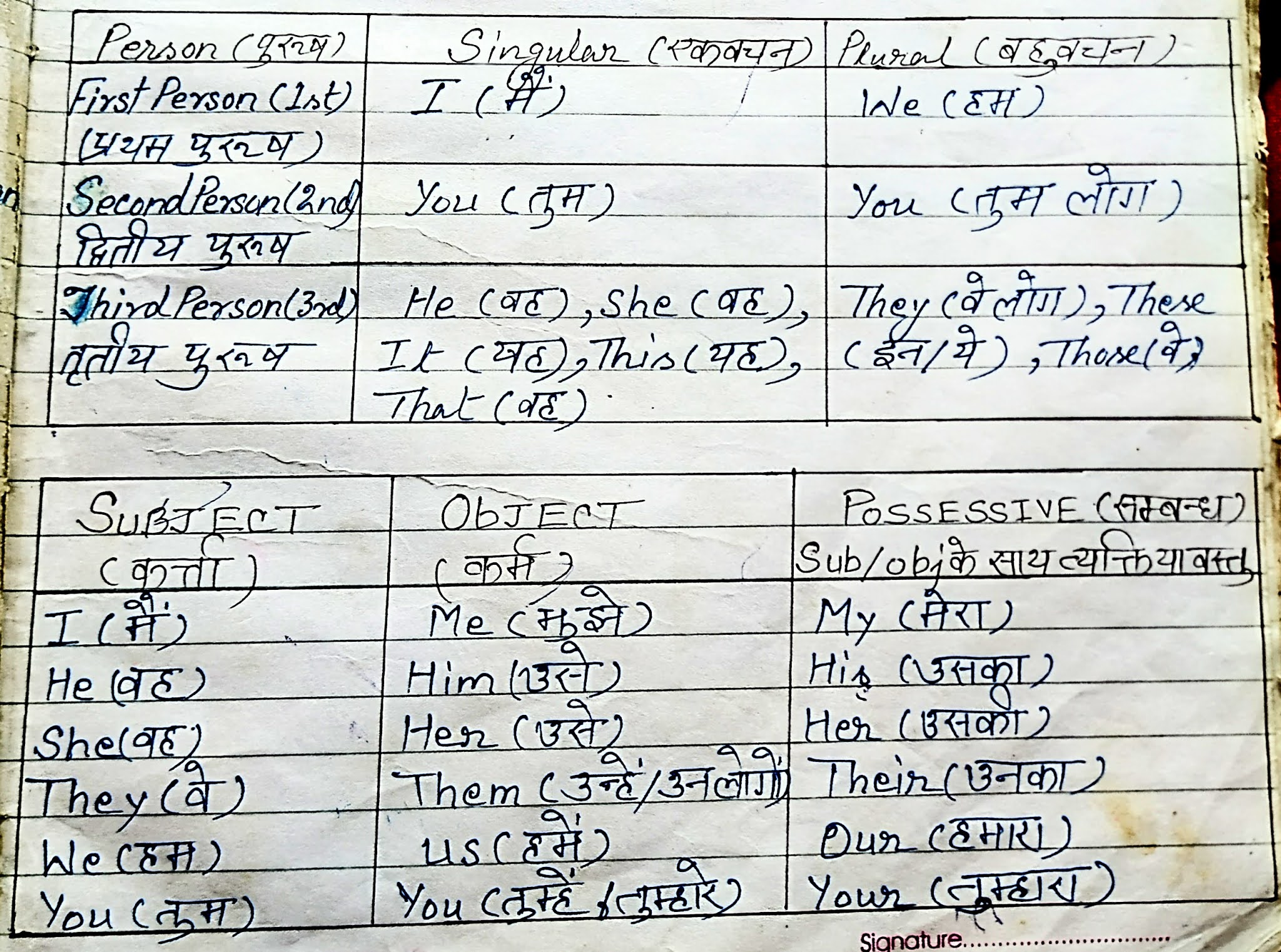
1. Personal Pronouns
I, we, you, he, she, it,they Personal Pronouns है।
* I, we, you, he, she, it and they are called personal pronouns.
a Personal relating to Persons (First Person/ Second Person/Third Person).
I,We -First Person Pronouns |
You -Second Person Pronoun |
He, She, It,They -Third Person के Pronouns हैं। इसलिए इन सातों Pronouns को Personal Pronouns कहा जाता है ।
Personal Pronouns के रूप case-wise बदलते हैं, जिन्हें इस सारणी से समझें -
Note 1. Personal Pronouns के सभी forms को आप यहाँ देख रहे My, Our, Your, His, Her, Its of Their Possessive Adjectives कहा जाता है क्योंकि ये किसी-न-किसी Noun के ठीक पहले प्रयुक्त होते हैं और Adjective की तरह कार्य करते हैं, जैसे
This is my book. Those are your books.
That is her book.
इन Possessive Adjectives में His और Her दो ऐसे शब्द हैं जिनका प्रयोग Pronoun की भाँति भी होता है, परंतु इस स्थिति में इनके ठीक बाद कोई भी Noun प्रयुक्त नहीं रहता, जैसे
This book is his.(his - Pronoun)
I know her.(her -Pronoun)
Note 2. Pronoun का प्रयोग Noun के बदले में होता है। इसलिए Pronoun के ठीक बाद कोई भी Noun प्रयुक्त नहीं रहता। जब Pronoun के ठीक बाद कोई Noun प्रयुक्त रहता है, तब वह Pronoun Adjective में परिवर्तित हो जाता है क्योंकि इस स्थिति में वह अपने बाद आनेवाले Noun को qualify करता है।
2. Possessive Pronouns
जिस Pronoun का प्रयोग अधिकार दिखाने के लिए किया जाता है, उसे Possessive Pronoun कहते हैं।
The Pronoun used to show possession is called a possessive pronoun.
mine, ours, yours, hers, his of theirs Possessive Pronouns हैं। इनका प्रयोग वस्तुओं पर अधिकार दिखाने के लिए किया जाता है, जैसा कि. इन उदाहरणों से स्पष्ट है
This book is mine.
These are ours. This saree is hers.
That book is yours.
Those are his. .
Those chairs are theirs.
Note: इनमें सिर्फ His एक ऐसा शब्द है जो Possessive Pronoun भी है और Possessive Adjective भी। जैसे
This is his car.(his- Possessive Adjective)
This car is his.(his–Possessive Pronoun )
3. Reflexive Pronouns
जब वाक्य में myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself itself और themselves के प्रयोग से काम करने का असर खुद कर्ता पर पड़ना प्रतीत होता है, तब इन्हें Reflexive Pronouns कहा जाता है।
The pronouns myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, itself and themselves are called reflexive pronouns when the action done by the subject turns back upon the subject.
I hurt myself.
मैंने अपने आपको चोट पहुँचाई।
We can help ourselves.
हमलोग अपने आपको मदद कर सकते हैं।
She ruined herself.
उसने अपने आपको बर्बाद किया।
यहाँ चोट पहुँचाने, मदद करने और बर्बाद करने का असर खुद कर्ता पर है। कर्ता ने खुद को चोट पहुंचाई। कर्ता खुद की मदद कर सकता है। कर्ता ने खुद को बर्बाद किया। अतः myself ourselves और herself इन वाक्यों में Reflexive Pronouns हैं।
4. Emphatic Pronouns
जब myself ourselves, yourself, yourselves, herself, himself, itself और themselves का प्रयोग वाक्य में किसी Noun या Pronoun पर जोर देने के लिए होता है, तब इन्हें Emphatic Pronouns कहा जाता है।
* Myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, herself, himself, itself and themselves are called emphatic pronouns when they are used for the sake of emphasis.
इन वाक्यों में इनके प्रयोग को देखें -
I killed the tiger myself. मैंने स्वयं (खुद) बाघ को मारा ।
He himself said so.
उसने स्वयं (खुद) ऐसा कहा।
She herself liked him. उसने स्वयं (खुद) उसे पसंद किया।
You can do it yourself. तुम इसे स्वयं (खुद) कर सकते हो।
Note: myself, ourselves, इत्यादि के spelling पर ध्यान दें। Singular Pronoun के साथ self लगता है और Plural Pronoun के साथ selves लगता है। you का प्रयोग जब एक व्यक्ति के लिए होता है, तब yourself और जब इसका प्रयोग अनेक व्यक्तियों के लिए होता है, तब yourselves का प्रयोग होता है। आप जानते हैं कि I, he, she और it Singular Number में हैं। we और they Plural Number में हैं। you का प्रयोग Singular और Plural दोनों वचनों में होता है।
EXERCISE 4
Direction: Tell which pronouns/adjectives in the following sentences are personal pronouns/ possessive pronouns/reflexive pronouns/ emphatic pronouns/ possessive adjectives
Examples:
(a) This is his pen.
(b) This pen is his.
(c) I myself did that.
(d) She washed herself.
(his - Possessive Adjective)
(his Possessive Pronoun) (I– Personal Pronoun,myself- Emphatic Pronoun)
(She Personal Pronoun.
herself-Reflexive Pronoun)
1. My mother loves me.
2. This book is hers.
3. Ours is black.
4. Our cow is black.
5. This garden is theirs.
6. It belongs to her.
7. This car is his.
8. This is his car.
9. Her face is beautiful.
10. Its colour is black.
11. She praised herself.
12. I hate myself.
13. She herself wrote this.
14. She herself did this.
15. I will do it myself.
16. He enjoyed himself.
17. The horse hurt itself.
18. They blamed themselves.
19. We ourselves can do it.
20. I myself locked the door.
5. Demonstrative Pronouns
जिस Pronoun का प्रयोग वस्तुओं या व्यक्तियों को सूचित, इंगित या निर्देशित करने के लिए किया जाता है, उसे Demonstrative Pronoun कहा जाता है।
* The pronoun used to point out the object or objects to which it refers is called a demonstrative pronoun.
This, That, These ,Those Demonstrative Pronouns हैं। इनका प्रयोग इन वाक्यों में देखें
This is a boy.
That is a girl.
These are balls.
Those are dolls.
Note: जब This, That, These, Those इत्यादि के ठीक बाद कोई Noun प्रयुक्त रहता है, तब इन्हें Demonstrative Adjectives कहा जाता है, जैसे–
This book is mine.
That book is yours.
These cows are red.
Those cows are brown.
6. Indefinite Pronouns
जिस Pronoun से किसी निश्चित व्यक्ति या वस्तु का बोध नहीं होता है, वह Indefinite Pronoun कहलाता है।
* An indefinite pronoun refers to persons or things in a general way and does not refer to any person or thing in particular.
ध्यान से देखने पर आप पाएंगे कि इनसे किसी निश्चित व्यक्ति या वस्तु का बोध नहीं होता है|
Somebody has stolen my pen.
Anybody can beat him.
Some are gentle.
All are foolish.
None can do this.
Many of them were killed.
One must not praise oneself.
None of them are good.
Nothing is perfect.
Any of you can take it.
Note:
जब some, all, many, one, any, इत्यादि के ठीक बाद कोई Noun प्रयुक्त रहता है, तब ये Adjectives कहलाते हैं। जैसे, इन वाक्यों में some, all, many, one और any Adjectives हैं—
Some boys are ready.
All things have their own values.
There were not many trees there.
I will take you there one day.
Any fool can do it.
7. Distributive Pronouns
जब each, either और neither का प्रयोग Pronoun के रूप में होता है, तब इन्हें Distributive Pronouns कहा जाता है।
* When each, either and neither are used as pronouns they are called distributive pronouns.
each- प्रत्येक
either -दोनों में से कोई एक
neither- दोनों में से कोई
each, either,neither Distributive Pronouns -
इन वाक्यों में प्रयुक्त शब्द each, either और neither Distributive Pronouns है।
Each of you is guilty.
Each of the boys is intelligent.
Either of you can take this book.
Neither of the two boys was absent.













































































































































Thanks 👍
ReplyDelete