CBSE CLASS 10 Science notes
CBSE CLASS 10 Science notes
CBSE Class 10 Science Book Chapter 1 “Chemical Reactions and Equations” Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) with Answers
Q1- Reaction of ‘magnesium’ with air is
A) Exothermic reaction
B) Endothermic reaction
C) Reversible reaction
D) Substitution reaction
Q2- What chemicals are used in fireworks?
A) Copper chloride
B) Calcium chloride
C) Barium chloride
D) All of above
Q3- When a magnesium ribbon is burnt in air, the ash formed is
A) Black
B) White
C) Yellow
D) Pink
Q4- Color of magnesium oxide is
A) White
B) Blue
C) Grey
D) Pink
Q5- If magnesium is gently heated, it forms
A) Magnesium oxide
B) Magnesium sulfide
C) Magnesium nitrite
D) Magnesium carbonate
Q6- When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water,
A) Calcium hydroxide is formed
B) White precipitate of CaO is formed
C) Lime water turns milky
D) Color of lime water disappears.
Q7- When crystals of lead nitrate are heated strongly in a dry test tube
A) Crystals immediately melt
B) A brown residue is left
C) White fumes appear in the tube
D) A yellow residue is left
Q8- Color of Solid magnesium is
A) Dark grey
B) Silver grey
C) Black
D) Whitish silver
Q9- Consider equations: Ca⁺²(aq) + 2OH‾(aq)→Ca(OH)₂ (s). Precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of
A) Green color
B) Blue color
C) Brown color
D) White color
Q10- In writing chemical equations, inclusion of state symbols shall be done while
A) Correct chemical formulae of reactants and products are written
B) The equation is being balanced to fulfill the law of conservation of mass
C) The equation has been balanced
D) The chemical formulae of products and reactants have been changed to bring about quick balancing
Q11- Consider equation: Pb⁺² (aq) + 2OH⁻ (aq) → Pb(OH)₂ (s). precipitate of lead (II) hydroxide will be of
A) Green color
B) Blue color
C) Brown color
D) White color
Q12- Consider equation: Cu⁺² (aq) + 2OH⁻(aq) → Cu(OH)₂ (s). precipitate of Copper Hydroxide (Cu(OH)₂) will be of
A) Green color
B) Blue color
C) Brown color
D) White color
Q13- Consider reaction: Na(s) + O₂(g) → Na₂O(s). Moles of sodium needed to balance equation would be
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Q14- Consider reaction: S(s) + O₂(g) → SO₂. state of SO₂ in this reaction is
A) Liquid
B) Solid
C) Gaseous
D) All Three
Q15- Consider reaction: P(s) + O₂(g) → P₄O₁₀(s). Moles of O₂(g) needed to balance equation will be
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 7
Q16- Consider reaction: Na(s) + O₂(g) → Na₂O. Moles of oxygen needed to balance equation are
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Q17- Consider reaction: Al(s) + O₂ (g) → Al₂O₃. Moles of Al(s) needed to balance equation are
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Q18- Which one of the given processes involves chemical reactions?
A) Storing of oxygen gas under pressure in a gas cylinder
B) Keeping petrol in a China dish in the open
C) Liquefaction of air
D) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature
Q19- In which of the given chemical equations, the abbreviations represent the correct states of the reactants and products involved at reaction temperature?
A) 2H₂ (l) + O₂ (l) → 2H₂O (g)
B) 2H₂ (g) + O₂ (l) → 2H₂O (g)
C) 2H₂ (g) + O₂ (g) → 2H₂O (l)
D) 2H₂ (g) + O₂ (g) → 2H₂O (g)
Q20- The reaction in which two compounds exchange their ions to form two new compounds is called
A) Displacement reaction
B) Combination reaction
C) Double displacement reaction
D) Redox reaction
Important Videos Links
Class 10 History Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 Civics Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 Economics Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 Geography Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 SST Sample Question Papers
Q21- On immersing an iron nail in CuSO₄ solution for a few minutes, you will observe
A) No reaction takes place
B) The color of solution fades away
C) The surface of iron nails acquire a black coating
D) The color of solution changes to green
Q22- Which of the given statements is not a physical change?
A) Boiling of water to give water vapour
B) Melting of ice to give water
C) Dissolution of salt in water
D) Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
Q23- An element X on exposure to moist air turns reddish-brown and a new compound Y is formed. The substances X and Y are
A) X = Fe, Y = Fe₂O₃
B) X = Ag, Y = Ag₂S
C) X = Cu, Y = CuO
D) X = Al, Y = Al₂O₃
Q24- The reaction of H₂ gas with oxygen gas to form water is an example of
A) Combination reaction
B) Redox reaction
C) Exothermic reaction
D) All of these reactions.
Q25- Rancidity can be prevented by
A) Adding antioxidants
B) Storing food away from light
C) Keeping food in refrigerator
D) All of these
Q26- In which of the given, heat energy will be evolved?
A) Electrolysis of water
B) Dissolution of NH₄Cl in water
C) Burning of L.P.G.
D) Decomposition of AgBr in the presence of sunlight
Q27- Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc taken in a test tube. The following observations are recorded. Point out the correct observation.
A) The surface of metal becomes shining
B) The reaction mixture turns milky
C) Odour of a pungent smelling gas is recorded
D) A colorless and odourless gas is evolved
Q28- Consider reaction is an example of
(a) 4NH₃ (g) + 5O₂ (g) → 4NO (g) + 6H₂O (g) (a). Displacement reaction,
(b) Combination reaction
(c) Redox reaction
(d) Neutralization reaction.
A) (A) & (D)
B) (B) & (C)
C) (A) & (C)
D) (C) & (D)
Q29- Which of the following statements about the given reaction are correct? 3Fe(s) + 4H₂O(g) → Fe₃O₄ (s) + 4H₂ (g)
(a) Iron metal is getting oxidized.
(b) Water is getting reduced.
(c) Water is acting as reducing agent.
(d)Water is acting as oxidizing agent.
A) (A), (B) & (C)
B) (C) & (D)
C) (A), (B) & (D)
D) (B) & (D)
Q30- Which of the following are exothermic processes?
(a) Reaction of water with quick lime
(b) Dilution of an acid
(c) Evaporation of water
(d) Sublimation of camphor (crystals)
A) (A) & (B)
B) (B) & (C)
C) (A) & (D)
D) (C) & (D)
Q31- A dilute ferrous sulphate solution was gradually added to the beaker containing acidified permanganate solution. The light purple color of the solution fades and finally disappears. Which of the given equation is the correct explanation for the observation?
A) KMnO₄ is an oxidizing agent, it oxidizes FeSO₄
B) FeSO₄ acts as an oxidizing agent and oxidizes KMnO₄
C) The color disappears due to dilution, no reaction is involved
D) KMnO₄ is an unstable compound and decomposes in the presence of FeSO₄ to a colourless compound
Q32- Which among the following statement(s) is /are true? Exposure of silver chloride to sunlight for a long duration turns grey due to-
(a) The formation of silver by decomposition of silver chloride.
(b) Sublimation of silver chloride.
(c) Decomposition of chlorine gas from silver chloride.
(d) Oxidation of silver chloride.
A) Only (A)
B) (A) & (C)
C) (B) & (C)
D) Only (D)
Q33- Solid calcium Oxide reacts vigorously with water to form calcium hydroxide accompanied by liberation of heat. This process is called slaking of lime. Calcium hydroxide dissolves in water to form its solution called lime water. Which among the following is are true about slaking of lime and the solution formed?
(a) It is an endothermic reaction.
(b) It is exothermic reaction.
(c) The pH of the resulting solution will be more than seven.
(d) The pH of the resulting solution will be less than seven.
A) (A) & (B)
B) (B) & (C)
C) (A) & (D)
D) (C) & (D)
Q34- Barium chloride on reacting with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of the reaction involved?
(a) Displacement reaction
(b) Precipitation reaction
(c) Combination reaction
(d) Double displacement reaction
A) Only (A)
B) Only (B)
C) Only (D)
D) (B) & (D)
Q35- Which of the following is (are) an endothermic process(es)?
(a) Dilution of sulphuric acid
(b) Sublimation of dry ice
(c) Condensation of water vapours
(d) Evaporation of water
A) Both (A) & (C)
B) Only (B)
C) Only (C)
D) Both (B) & (D)
Q36- In the double displacement reaction between aqueous potassium iodide and aqueous lead nitrate, a yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed. While performing the activity if lead nitrate is not available, which of the given can be used in place of lead nitrate?
A) Lead sulphate (insoluble)
B) Lead acetate
C) Ammonium nitrate
D) Potassium sulphate
Q37- Which of the given gases can be used for storage of fresh sample of an oil for a long time?
A) Carbon dioxide or oxygen
B) Nitrogen or oxygen
C) Carbon dioxide or helium
D) Helium or nitrogen
Q38- Fatty foods become rancid due to the process of ________
A) Oxidation
B) Corrosion
C) Reduction
D) Hydrogenation
Q39- Which information is not conveyed by a balanced chemical equation?
A) Physical states of reactants and products
B) Symbols and formulae of all the substances involved in a particular reaction
C) Number of atoms/molecules of the reactants and products formed
D) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not
Q40- The chemical formula of lead sulphate is
A) Pb₂SO₄
B) Pb(SO₄)₂
C) PbSO₄
D) Pb₂(SO₄)₃
Q41- Chemically, rust is
A) Hydrated ferrous
B) Only ferric oxide
C) Hydrated ferric oxide
D) None of these
Q42- Both CO₂ and H₂ gases are
A) Heavier than air
B) Colourless
C) Acidic in nature
D) Soluble in water
Q43- Which of the given gases can be used for storage of fresh samples of an oil for a long time?
A) Carbon dioxide or oxygen
B) Nitrogen or helium
C) Helium or oxygen
D) Nitrogen or oxygen
Q44- In the decomposition of lead (II) nitrate to give lead (II) oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen gas, the coefficient of nitrogen dioxide (in the balanced equation) is
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Q45- We store silver chloride in a dark coloured bottle because it is
A) A white solid
B) Undergoes redox reaction
C) To avoid action by sunlight
D) None of the above
Q46- Silver article turns black when kept in the open for a few days due to formation of
A) H₂S
B) AgS
C) AgSO₄
D) Ag₂S
Q47- When crystals of lead nitrate are heated strongly in a dry test tube
A) Crystals immediately melt
B) A brown residue is left
C) White fumes appear in the tube
D) A yellow residue is left
Q48- Which of the given products is formed when calcium oxide reacts with water?
A) Slaked lime
B) Carbon dioxide
C) Calcium oxide
D) Oxygen gas
Q49- What is the other name for quick lime?
A) Calcium hydroxide
B) Calcium oxide
C) Carbon dioxide
D) Sodium oxide
Q50- What is the chemical name for slaked lime?
A) Calcium carbonate
B) Calcium oxide
C) Calcium hydroxide
D) Carbon monoxide
Class 10 Science
MCQs
Chapter 2
Acids Bases and Salts
1. What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube?
(i) Temperature of the solution decreases
(ii) Temperature of the solution increases
(in) Temperature of the solution remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
Answer: d
2. When hydrogen chloride gas is prepared on a humid day, the gas is usually passed through the guard tube containing calcium chloride. The role of calcium chloride taken in the guard tube is to
(a) absorb the evolved gas
(b) moisten the gas
(c) absorb moisture from the gas
(d) absorb Cl– ions from the evolved gas
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: Reason: Guard tube drys (absorbs water) from calcium chloride on a humid day.
3. Which one of the following salts does not con-tain water of crystallisation?
(a) Blue vitriol
(b) Baking soda
(c) Washing soda
(d) Gypsum
Answer
Answer: b
4. In terms of acidic strength, which one of the following is in the correct increasing order?
(a) Water < Acetic acid < Hydrochloric acid
(b) Water < Hydrochloric acid < Acetic acid
(c) Acetic acid < Water < Hydrochloric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid < Water < Acetic acid
Answer
Answer: a
5. What is formed when zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide?
(a) Zinc hydroxide and sodium
(b) Sodium zincate and hydrogen gas
(c) Sodium zinc-oxide and hydrogen gas
(d) Sodium zincate and water
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason: Zn + 2NaOH → Ma2Zn02 (Sodium Zincate) + H2
6. Tomato is a natural source of which acid?
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Citric acid
(c) Tartaric acid
(d) Oxalic acid
Answer
Answer: d
7. Brine is an
(a) aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide
(b) aqueous solution of sodium carbonate
(c) aqueous solution of sodium chloride
(d) aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate
Answer
Answer: c
8. Na2CO3 . 10H2O is
(a) washing soda
(b) baking soda
(c) bleaching powder
(d) tartaric acid
Answer
Answer: a
9. At what temperature is gypsum heated to form Plaster of Paris?
(a) 90°C
(b) 100°C
(c) 110°C
(d) 120°C
Answer
Answer: b
10. How many water molecules does hydrated cal-cium sulphate contain?
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 7
(d) 2
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Reason: Chemical formula of hydrated calcium sulphate or gypsum is CaSO4.2H2O
11. Sodium carbonate is a basic salt because it is a salt of a
(a) strong acid and strong base
(b) weak acid and weak base
(c) strong acid and weak base
(d) weak acid and strong base
Answer
Answer: d
12. Alkalis are
(a) acids, which are soluble in water
(b) acids, which are insoluble in water
(c) bases, which are insoluble in water
(d) bases, which are soluble in water
Answer
Answer: d
13. Which of the following statements is correct about an aqueous solution of an acid and of a base?
(i) Higher the pH, stronger the acid
(ii) Higher the pH, weaker the acid
(in) Lower the pH, stronger the base
(iv) Lower the pH, weaker the base
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Reason: Stronger the acid, lesser is the pH. Stronger the base, higher is the pH.
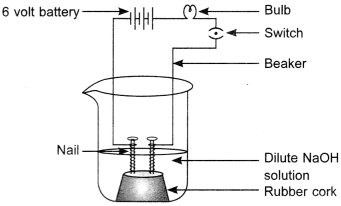
14. The apparatus given in the adjoining figure was set up to demonstrate electrical conductivity.
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Bulb will not glow because electrolyte is not acidic.
(ii) Bulb will glow because HCl is a strong acid and furnishes ions for conduction.
(iii) Bulb will not glow because circuit is incomplete.
(iv) Bulb will not glow because it depends upon the type of electrolytic solution.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer
Answer: c
15. Lime water reacts with chlorine to give
(a) bleaching powder
(b) baking powder
(c) baking soda
(d) washing soda
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
16. Nettle sting is a natural source of which acid?
(a) MetiWanoic acid
(b) Lactic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Tartaric acid
Answer
Answer: a
17. Tooth enamel is made up of
(a) calcium phosphate
(b) calcium carbonate
(c) calcium oxide
(d) potassium
Answer
Answer: a
18. What is the pH range of our body?
(a) 7.0 – 7.8
(b) 7.2 – 8.0
(c) 7.0 – 8.4
(d) 7.2 – 8.4
Answer
Answer: a
19. Rain is called acid rain when its:
(a) pH falls below 7
(b) pH falls below 6
(c) pH falls below 5.6
(d) pH is above 7
Answer
Answer: c
20. Sodium hydroxide is a
(a) weak base
(b) weak acid
(c) strong base
(d) strong acid
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: Reason: Sodium hydroxide ionises in water and produces a large amount of hydroxide ions.
21. An aqueous solution turns red litmus solution blue. Excess addition of which of the following solution would reverse the change?
(a) Baking powder
(b) Lime
(c) Ammonium hydroxide solution
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Answer
Answer: d
22. When copper oxide and dilute hydrochloric acid react, colour changes to
(a) white
(b) bluish-green
(c) blue-black
(d) black
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason: Blue-green colour of solution is due to the formation of copper (II) chloride.
23. Sodium hydroxide is used
(a) as an antacid
(b) in manufacture of soap
(c) as a cleansing agent
(d) in alkaline batteries
Answer
Answer: b
24. Sodium hydroxide turns phenolphthalein solution
(a) pink
(b) yellow
(c) colourless
(d) orange
Answer
Answer: a
25. Chemical formula of washing soda is
(a) Na2C03 . 7H2O
(b) Na2C03 . 5H2O
(c) Na2C03 . 2H2O
(d) Na2C03 . 10H2O
Answer
Answer: d
Lesson-3
1. Which of the given properties is generally not shown by metals?
A. Electrical conduction
B. Sonorous in nature
C. Dullness
D. Ductility
2. The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wire is known as
A. Ductility
B. Malleability
C. Sonorousity
D. Conductivity
3. Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same?
(a) Good thermal conductivity
(b) Good electrical conductivity
(c) Ductility
(d) High melting point
A. (A) & (B)
B. (A) & (C)
C. (B) & (C)
D. (A) & (D)
Also See: CBSE Class 10 English MCQs
4. Which one of the given metals does not react with cold as well as hot water?
A. Na
B. Ca
C. Mg
D. Fe
5. Which of the given oxide(s) of iron would be obtained on prolonged reaction of iron with steam?
A. FeO
B. Fe₂O₃
C. Fe₃O₄
D. Fe₂O₃ and Fe₃O₄
6. What happens when calcium is treated with water?
(a) It does not react with water
(b) It reacts violently with water
(c) It reacts less violently with water
(d) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium
A. (A) & (D)
B. (B) & (C)
C. (A) & (B)
D. (C) & (D)
7. Generally metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen gas. Which of the given acids does not give hydrogen gas on reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg)?
A. H₂SO₄
B. HCl
C. HNO₃
D. All the these
8. The composition of aqua-regia is
A. Dil.HCl : Conc. HNO₃ = 3 : 1
B. Conc.HCl : Dil. HNO₃ = 3 : 1
C. Conc.HCl : Conc. HNO₃ = 3 : 1
D. Dil.HCl : Dil. HNO₃ = 3 : 1
9. Which of the following are not ionic compounds?
(a) KCl
(b) HCl
(c) CCl₄
(d) NaCl
A. (A) & (B)
B. (B) & (C)
C. (C) & (D)
D. (A) & (C)
10. Which one of the given properties is not generally exhibited by ionic compounds?
A. Solubility in water
B. Electrical conductivity in solid state
C. High melting and boiling points
D. Electrical conductivity in molten state
11. Which of the following metals exists in its native state in nature?
(a) Cu
(b) Au
(c) Zn
(d) Ag
A. (A) & (B)
B. (B) & (C)
C. (B) & (D)
D. (C) & (D)
12. Metals are refined by using different methods. Which of the following metals are refined by electrolytic refining?
(a) Au
(b) Cu
(c) Na
(d) K
A. (A) & (B)
B. (A) & (C)
C. (B) & (C)
D. (C) & (D)
13. Silver articles become black on prolonged exposure to air. This is due to the formation of
A. Ag₃N
B. Ag₂O
C. Ag₂S
D. Ag₂S and Ag₃N
14. Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating with a thin layer of
A. Gallium
B. Aluminium
C. Zinc
D. Silver
15. Stainless steel is very useful material for our life. In stainless steel, iron is mixed with
A. Ni and Cr
B. Cu and Cr
C. Ni and Cu
D. Cu and Au
16. If copper is kept open in air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of
A. CuSO₄
B. CuCO₃
C. Cu(NO₃)₂
D. CuO
17. Generally, metals are solid in nature. Which one of the given metals is found in liquid state at room temperature?
A. Na
B. Fe
C. Cr
D. Hg
18. Which of the given metals are obtained by electrolysis of their chlorides in molten state ?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Fe
(d) Cu
A. (A) & (D)
B. (C) & (D)
C. (A) & (C)
D. (A) & (B)
Also See: CBSE Class 10 History MCQs
19. Generally, non-metals are not lustrous. Which of the given nonmetals is lustrous?
A. Sulphur
B. Oxygen
C. Nitrogen
D. Iodine
20. Which one of the given four metals would be displaced from the solution of its salts by other three metals?
A. Mg
B. Ag
C. Zn
D. Cu
21. 2 ml each of concentrated HCl, HNO₃ and a mixture of concentrated HCl and concentrated HNO₃ in the ratio of 3 : 1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A and B but the metal got dissolved in test tube C respectively. The metal could be
A. Al
B. Au
C. Cu
D. Pt
22. An alloy is
A. An element
B. A compound
C. A homogeneous mixture
D. A heterogeneous mixture
23. An electrolytic cell consists of
(a) Positively charged cathode
(b) Negatively charged anode
(c) Positively charged anode
(d) Negatively charged cathode
A. (A) & (B)
B. (C) & (D)
C. (A) & (C)
D. (B) & (D)
24. During electrolytic refining of zinc, it gets
A. Deposited on cathode
B. Deposited on anode
C. Deposited on cathode as well as anode
D. Remains in the solution
25. An element A is soft and can be cut with a knife. This is very reactive to air and cannot be kept open in air. It reacts vigorously with water. Identify the element
A. Mg
B. Na
C. P
D. Ca
26. Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or nonmetal. Which among the given alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
A. Brass
B. Bronze
C. Amalgam
D. Steel
27. Which among the given statements is incorrect for magnesium metal?
A. It burns in oxygen with a dazzling white flame
B. It reacts with cold water to form magnesium oxide and evolves hydrogen gas
C. It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and evolves hydrogen gas
D. It reacts with steam to form magnesium hydroxide and evolves hydrogen gas
28. Which among the given alloys contains mercury as one of its constituents?
A. Stainless steel
B. Alnico
C. Solder
D. Zinc amalgam
Important Videos Links
Class 10 History Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 Civics Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 Economics Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 Geography Lesson Video Explanation
Class 10 SST Sample Question Papers
29. Reaction between X and Y, forms compound Z. X loses electron and Y gains electron. Which of the given properties is not shown by Z?
A. Has high melting point
B. Has low melting point
C. Conducts electricity in molten state
D. Occurs as solid
30. The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are X – 2, 8; Y – 2, 8, 7 and Z – 2, 8, 2. Which of the given is correct?
A. X is a metal
B. Y is a metal
C. Z is a non-metal
D. Y is a non-metal & Z is a metal
31. Although metals form basic oxides, which of the given metals form an amphoteric oxide?
A. Na
B. Ca
C. Al
D. Cu
32. Generally, non-metals are not conductors of electricity. Which of the given is a good conductor of electricity?
A. Diamond
B. Graphite
C. Sulphur
D. Fullerene
33. Electrical wires have a coating of an insulating material. The material generally used is
A. Sulphur
B. Graphite
C. PVC
D. All can be used
34. Which of the given non-metals is a liquid?
A. Carbon
B. Bromine
C. Phosphors
D. Sulphur
35. Which of the given can undergo a chemical reaction?
A. MgSO₄ + Fe
B. ZnSO₄ + Fe
C. MgSO₄ + Pb
D. CuSO₄ + Fe
36. Which of the given metals is present in the anode mud during the electrolytic refining of copper?
A. Sodium
B. Aluminium
C. Gold
D. Iron
37. An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. The compound is soluble in water. The element is likely to be
A. Calcium
B. Carbon
C. Iron
D. Silicon
38. The second most abundant metal in the earth’s crust is
A. Oxygen
B. Silicon
C. Aluminium
D. Iron
39. An alloy of Zn and Cu is dissolved in dil. HCl. Hydrogen gas is evolved. In this evolution of gas
A. Only zinc reacts with dil. HCl
B. Only copper reacts with dil. HCl
C. Both zinc and copper react with dil. HCl
D. Only copper reacts with water
40. A greenish coating develops on copper utensils due to formation of
A. CuCO₃
B. Cu(OH)₂
C. Cu(OH)₂.CuCO₃
D. CuO
41. Rusting of iron takes place in
A. Ordinary water
B. Distilled water
C. Both ordinary & Distilled water
D. None of these
42. The bronze medals are made up of
A. Cu and Zn
B. Zn and Ni
C. Cu and Sn
D. Cu, Zn, Tn
43. Silver articles become black on prolonged exposure to air. This is due to the formation of
A. Ag₂O
B. Ag₂S
C. AgCN
D. Ag₂O and Ag₂S
44. During smelting, an additional substance is added which combines with impurities to form a fusible product known as
A. Slag
B. Mud
C. Gangue
D. Flux
45. A student placed an iron nail in copper sulphate solution. He observed the reddish brown coating on the iron nail which is
A. Soft and dull
B. Hard and flading
C. Smooth and shining
D. Rough and granular
46. Which among the given alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
A. Brass
B. Amalgam
C. Gunmetal
D. None of these
47. An aluminium strip is kept immersed in freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution taken in a test tube, the change observed is that
A. Green solution slowly turns brown
B. Lower end of test tube become slightly warm
C. A colourless gas with the smell of burning sulphur is observed
D. Light green solution changes to blue
48. Which of the given metals cannot be extracted using smelting?
A. Fe
B. Al
C. Zn
D. Pb
49. In general, the number of electrons in the outermost shell of a metal atom is
A. 1
B. 1 to 3
C. 5 to 8
D. 8
50. Aluminum is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminum are responsible for the same?
(a) Good thermal conductivity
(b) Good electrical conductivity
(c) Ductility
(d) High melting point
A. (A) & (B)
B. (A) & (C)
C. (B) & (C)
D. (A) & (D)
Answer Key for
Class 10
Science Book
Chapter 3
Metals and Non-Metals
MCQs
Q. No. Ans. Q. No. Ans. Q. No. Ans. Q. No. Ans. Q. No. Ans.
1 C 11 C 21 B 31 C 41 C
2 A 12 D 22 C 32 B 42 C
3 D 13 C 23 B 33 C 43 B
4 D 14 C 24 A 34 B 44 A
5 C 15 A 25 B 35 D 45 D
6 D 16 B 26 D 36 D 46 B
7 C 17 D 27 B 37 C 47 A
8 A 18 D 28 D 38 D 48 B
9 B 19 D 29 B 39 A 49 B
10 B 20 B 30 D 40 A 50 D
Light Reflection
and Refraction
MCQs Class 10 Science
Chapter 10
Q1- In an astronomical telescope the focal length of objective lens is 100 cm and that of eyepiece is 2 cm. The magnifying power of the telescope for the normal eye is :
A) 1/50
B) 100
C) 10
D) 50
Q2- A ray reflected successively from two plane mirrors inclined at a certain angle undergoes a deviation of 3000 . Then the number of images observable is :
A) 60
B) 12
C) 11
D) 5
Q3- Light with wavelength of 6000 A0 units has a frequency :
A) 5 x 10¹⁷ Hz
B) 5 x 10¹⁶ Hz
C) 5 x 10¹⁵ Hz
D) 5 x 10¹⁴ Hz
Q4- Large aperture objects are used in telescopes because they :
A) Have better dispersion
B) Have less aberration
C) Have better resolution
D) Can see larger objects
Q5- At what distance from a screen will a 27 Cd lamp provide the same illumination as a 75 Cd lamp 15 m from the screen ?
A) 9 m
B) 6 m
C) 3 m
D) 1 m
Q6- Monochromatic light of frequency 5 x 10⁴ Hz travelling in vacuum enters a medium of refractive index 1.5. Its wavelength in the medium is :
A) 5000 A0
B) 4000 A0
C) 5500 A0
D) 6000 A0
Q7- Two thin lenses, one of focal length +60 cm and the other of focal length -20 cm are kept in contact. Their combined focal length is
A) Minus 30 cm
B) Plus 30 cm
C) Minus 15 cm
D) Plus 30 cm
Q8- The focal length of a concave mirror is f and the distance of the object to the principal focus is p . Then the ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object is :
A) p/p
B) p/f
C) fp
D) (?pf)
Q9- For which of the given is luminous efficiency maximum ?
A) Sodium vapour lamp
B) Mercury vapour lamp
C) Arc lamp
D) Tungsten filament lamp
Q10- When light travels from one medium to other whose refractive index is different, then which of the given will change?
A) Wavelength and velocity
B) Frequency and wavelength
C) Frequency and wavelength
D) Frequency, wavelength and velocity
Q11- A blue object on a white background when seen through a blue filter will appear :
A) Black on a blue background
B) Blue on a white background
C) Blue on a red background
D) Invisible
Q12- In a photometer two sources of light when placed at 30 and 50 cm respectively produce shadow of equal intervals. Their candles are in the ratio of
A) 9/25
B) 16/25
C) 3/5
D) 6/25
Q13- Spherical air bubble in water will act as :
A) A concave lens
B) A convex lens
C) Plane-concave lens
D) Plane glass plate
Q14- A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of incidence 300 . The ray after reflection is deviated through :
A) 30 degree
B) 60 degree
C) 90 degree
D) 120 degree
Q15- The number of images observable between two parallel mirrors is :
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) Infinity
Q16- f = r/2 is valid :
A) For convex mirrors but not for concave mirrors
B) For concave mirrors but not for convex mirrors
C) For both convex and concave mirrors
D) Neither for convex mirrors nor for concave mirrors
Q17- Laser is :
A) Coherent and monochromatic only
B) Intense and monochromatic only
C) Intense and coherent only
D) Intense coherent and monochromatic
Also See: CBSE Class 10 History MCQs
Q18- The focal length of a plano-convex lens having a radius of curvature of 10 cm for convex surface and a refractive index of 1.5 will be :
A) 20 cm
B) 15 cm
C) 10 cm
D) 5 cm
Q19- If in a plano-convex lens the radius of curvature of the convex surface is 10 cm and the focal length of the lens is 30 cm then the refractive index of the material of lens will be :
A) 1.33
B) 3
C) 1.66
D) 1.5
Q20- Total internal reflection of light is possible when light enters from :
A) Water to air
B) Air to water
C) Vacuum to air
D) Air to glass
Q21- Magnifying power of a compound microscope is the ratio of the angle formed by the final image to the angle formed by the object when :
A) Image is at the least distance of distinct vision and object may be anywhere
B) Object and image are both at infinity
C) Object and image are both at the least distance of distinct vision
D) Object is placed at the least distance of distinct vision and image may be at any place
Q22- When white light moves through vacuum :
A) Violet has greater speed than red
B) Red has greater speed than violet
C) All colours have the same speed
D) Different colours have different random speeds
Q23- Refractive index of a material for infrared light is :
A) Equal to that for red colour of light
B) Equal to that for ultraviolet light
C) Less than that for ultraviolet light
D) Greater than that for ultraviolet light
Q24- A hole is made in a convex lens . Then :
A) A hole appears in the image
B) Image size decreases
C) Image intensity decreases
D) No change
Q25- Critical angle of light passing from glass to air is minimum for :
A) Red
B) Green
C) Yellow
D) Violet
Q26- Which of the given is not true of an image formed by a plane mirror ?
A) It is erect
B) It is virtual
C) It is diminished
D) It is at the same distance as the object
Q27- Two lenses of power +3 and -1 diopters are placed in contact. The focal length of the combined lens is :
A) 100 cm
B) 25 cm
C) 50 cm
D) 30.3 cm
Q28- The focal length of a concave mirror is 50 cm. To obtain an inverted image two times the size of the object the object should be placed at :
A) 50 cm
B) 63 cm
C) 72 cm
D) 75 cm
Q29- What is the minimum distance between an object and its virtual image in case of a concave lens ?
A) 0
B) f
C) 2f
D) 4f
Q30- The focal length of lens depends on :
A) The radii of curvature of its surfaces
B) The refractive index of its material
C) The refractive index of the medium surrounding
D) All of the these factors
Q31- A parallel beam of light is incident on a converging lens parallel to its principal axis. As we move away from the lens on the other side on its principal axis the intensity of light
A) Remains constant
B) Continuously increases
C) Continuously decreases
D) First increases and then decreases
Q32- Using a convex lens, a clear image of candle flame is produced on a screen. How many other clear images can be received on this screen if only the lens is to be shifted ?
A) A large number
B) Only one more
C) Two more
D) None of these
Q33- A convex lens of power P is immersed in a water . How will its power change ?
A) Increases
B) Remain unchanged
C) Decreases
D) Increases for red colour and decreases for blue colour
Q34- In order to increase the magnifying power of a microscope :
A) The objective should have larger focal length and eyepiece should have small focal length
B) The focal power of the objective and the eyepiece should be larger
C) The objective should have small focal length and the eyepiece should have larger focal length
D) The focal length of the objective and the eyepiece should be large
Q35- The focal length of the object of microscope is
A) Greater than the focal length of eyepiece
B) Less than the focal length of eyepiece
C) Equal to the focal length of eyepiece
D) Arbitrary
Q36- In which of the given cases do we get very strong reflected rays and very weak refracted rays ?
A) Light passing from air to glass
B) Light passing from water to glass
C) Light passing from glass to diamond
D) Light passing from water to air
Q37- Light waves spreading from two sources produce interference only if they are :
A) Coherent
B) Transverse
C) Longitudinal
D) None of these
Q38- Which of the given can produce a virtual image larger in size than the object ?
A) Convcave lens
B) Convex lens
C) Convex concave lens
D) None of these
Q39- A lens has a power of +0.5D. It is:
A) A concave lens of local length 5 m
B) A convex lens of focal length 2 m
C) A convex lens of focal length 5 m
D) A concave lens of focal length 2 m
Q40- On heating a liquid the refractive index generally:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Does not change
D) Increases or decreases depending upon rate of heating
Q41- A diverging lens will produce
A) Always a virtual image
B) Real or virtual image
C) Always real image
D) None of these
Q42- A hunter wants to shoot a fish whose image can be seen through clear water. It is to be aimed:
A) Below the image of fish
B) Above the image of fish
C) Directly towards the image
D) In any direction
Q43- When light enters from a rarer medium to a denser medium:
A) Its frequency changes
B) Wavelength does not change
C) Its wavelength changes
D) Both wavelength and frequency change
Q44- Refractive index:
A) Depends on the wavelength of light used to measure
B) Is actual property of the substance
C) Depends on the angle of incidence
D) None of these
Q45- An object is approaching a plane mirror at 5 cm/s. A stationary observer sees the image. At what speed will the image appear to approach the stationary observer?
A) 20 cm/s
B) 10 cm/s
C) 15 cm/s
D) 5 cm/s
Q46- If a diverging lens is to be used to form an image which is one fourth of the size of the object where must the object be placed?
A) 3f
B) 4f
C) 2f
D) F
Q47- Which of the given is NOT paired correctly?
A) Solar furnace-concave mirror
B) Rear -view mirror-convex mirror
C) Magnifying glass -convex lens
D) None of these
Q48- A concave lens from the image of an object which is :
A) Virtual inverted and diminished
B) Virtual upright and diminished
C) Virtual inverted and enlarged
D) Virtual upright and enlarged
Q49- A man runs towards the plane mirror at 2 m/s. The relative speed of his image with respect to him will be:
A) 4 ms⁻¹
B) 2 ms⁻¹
C) 8 ms⁻¹
D) 10 ms⁻¹
Q50- In order to obtain a magnification of, -0.6 (minus 0.6) with a concave mirror, the object must be placed:
A) At the focus
B) Between pole and focus
C) Between focus and centre of curvature
D) Beyond the centre of curvature
1. The image formed by retina of human eye is :
A. Virtual and erect
B. Real and inverted
C. Virtual and inverted
D. Real and erect
2. The change in focal length of human eye is caused due to –
A. Ciliary muscles
B. Pupil
C. Cornea
D. Iris
3. The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is :
A. 25m
B. 20m
C. 25cm
D. 20cm
4. The persistence of vision for human eye is-
A. 1/10th of a sec
B. 1/16th of a sec
C. 1/6th of a sec
D. 1/18th of a sec
5. The light sensitive cell present on retina and is sensitive to the intensity of light is :
A. cones
B. Rod cell
C. Both cone and rod cells
D. None
6. The phenomenon of light responsible for the working of human eye is :
A. Reflection
B. Refraction
C. Power of accommodation
D. Persistence of vision
7. Which of the following colours is least scattered by fog, dust or smoke :
A. Violet
B. Blue
C. Red
D. Yellow
8. The coloured light that reflects most while passing through a prism is :
A. yellow
B. Violet
C. Blue
D. Red
9. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by :
A. Ciliary muscles
B. Pupil
C. Cornea
D. Iris
10. The part of the eye which refracts light entering the eye from external objects :
A. Lens
B. Cornea
C. Iris
D. Pupil
11. The variation of focal length to form a sharp image on the retina is called ----.
A. Accommodation
B. Aperture
C. Retina control
D. Sutter
12. In human eye image is formed :
A. Behind retina
B. In front of retina
C. On retina
D. In between lens and retina
13. Light enters eye through a transparent membrane called :
A. Cornea
B. Pupli
C. Iris
D. Retina
14. Colored portion of eye that controls amount of light reaching retina is called :
A. Cornea
B. Pupil
C. Retina control
D. Iris
15. Human eye acts like a -------.
A. Endoscope
B. Camera
C. Telescope
D. Microscope
16. The passage through which tears pass is :
A. Cornea
B. Tear gland
C. Tear duct
D. Eyeball
17. The part of eye that is a messenger of electrochemical signals from eye to brain is called :
A. Blood vessel
B. Optic nerve
C. Iris
D. Cornea
18. Thing that shuts automatically to protect eyes is known as :
A. Eyelash
B. Eyelid
C. Iris
D. Cornea
19. Ability of combination of dual vision of eyes is called :
A. Dim vision
B. Concave vision
C. Binocular vision
D. Bright vision
20. For a young adult with normal vision the far point is :
A. 20cm
B. 20m
C. 20Km
D. Infinity
21. Sunlight is a mixture of __ visible colours
A. 5
B. 6
C. 7
D. none
22. The effect of glass prism is only to separate the seven colours of
A. White light
B. light from bulb
C. Sunlight
D. All
23. The __ colour is at the top and ____ colour is at the bottom of spectrum.
A. Red, Violet
B. Red, Blue
C. Violet, red
D. None
24. Who discovered the experiments with glass prism that white light consists of seven colours
A. Newton
B. Faraday
C. Maxwell
D. Young
25. The light that refracts most while passing through a prism
A. Red
B. Violet
C. Indigo
D. Yellow
26. The rod cells responds to
A. Colour of light
B. Source of light
C. Intensity of light
D. None
27. Which of the following colours is the least deviated on passing through a prism :
A. Red
B. Yellow
C. Violet
D. Indigo
28. Cornea is a transparent spherical structure which ____
A. Reflects light
B. Refracts light
C. Scatters light
D. None
29. The image on the retina remains for 1/16th of sec. This is called as:
A. Accomodation
B. Persistence of vision
C. Both a and b
D. None
30. The middle vascular layer that darkens the eye from inside and prevents internal reflection is :
A. Choroid
B. Sclera
C. Retina
D. Cornea
31. The eye lens is a
A. Transparent double convex lens
B. Transparent double concave lens
C. Transparent concave convex lens
D. None
32. The eye lens contains a liquid called :
A. Aqueous humour
B. Peroxide
C. Vitreous humour
D. None
33. Long sightedness is caused by eyeball being too short. It can be corrected by :
A. Using convergent lens
B. Plane mirror
C. Divergent lens
D. None
34. Astigmatism occurs when the cornea does not have a truly spherical shape. The defect can be cured by :
A. Concave lens
B. Cylindrical shape
C. Convex lens
D. Plane convex lens
35. The power of lens being +4 D, suggests that it is :
A. Convex lens
B. Plane convex lens
C. Concave lens
D. none
36. When an object moves towards a convex lens the size of image _____.
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. First decreases then increases
D. Remains the same
37. When Newton colour disc is rotated fast, the different colours _____.
A. Can be separated
B. Can be differentiated
C. Can not be differentiated
D. None
38. When a ray passes through a prism ______.
A. It goes undeviated
B. It remain parallel to a base
C. It bends towards the base
D. None
39. The angle at which the ray gets deviated is called :
A. Angle of deviation
B. Angle of dispersion
C. Angle emergence
D. refracted angle
40. At a particular minimum angle of deviation, the prism is under :
A. Maximum deviation position
B. Minimum or maximum deviation position
C. Minimum deviation position
D. None
41. At a particular minimum value of angle of deviation, the refracted ray becomes :
A. Parallel to base of prism
B. Perpendicular to base of prism
C. Inclined at 45degrees w.r.t base of prism
D. None
42. The angle between two refracting surfaces of prism is :
A. Prism
B. Emergence
C. Deviation
D. Incidence
43. A transparent refracting material which is bounded by two plane refracting surfaces is :
A. Prism
B. Convex lens
C. Glass slab
D. None
44. The ratio of real depth to apparent depth is called :
A. Refractive index
B. Critical angle
C. Lateral displacement
D. None
45. The image formed by retina of human eye is :
A. Permanent
B. temporary
C. Blurred
D. None
46. The property related to the sense of continuity of vision is called :
A. Persistence of vision
B. Colour blindness
C. Optical illusion
D. None
47. When the muscles are relaxed, the eye lens is ______ and the distant objects can be seen clearly.
A. Thin
B. Thick
C. Inclined
D. None
48. When looking at nearby objects the muscles ____ the eye lens so as to __ its focal length.
A. Compresses, increases
B. Compresses, decreases
C. Expands, increase
D. Expands, decrease
49. The muscular diaphragm that controls the sides of pupil is :
A. Cornea
B. Ciliary muscles
C. Iris
D. Retina
50. Having two eyes facilities :
A. Increasing the field view
B. Three dimensional view
C. Developing concept of distance
D. All









Comments
Post a Comment